Key Takeaways
- Climate change exacerbates water scarcity and water related hazards.
- Watershed management guarantees water and soil conservation for food and water security.
- Healthier watersheds support ecosystems and advance climate change resilience
- Development projects should incorporate watershed management into their program design to support climate change resilience.
- Nigeria has about 277 watersheds with only 57 of them prime for development under sustainable management practices to foster climate resilience.
INTRODUCTION
In 2012, Nigeria suffered an estimated loss of $16.9b in damaged properties, oil production, agriculture and others due to flood events. Since then, large flooding events have become recurrent every year. The damages caused by these challenges are directly associated with poor watershed management and increasing climate change impacts in Nigeria (1,2). The last major flood in Nigeria which happened in Borno State exemplifies the phenomenon.
But what exactly are watersheds? Watersheds are the most valuable land units in any given location where water, soil and other associated resources are found in abundance for productive human use. A watershed is defined as the area where a river catches its water. The incoming waters that form the streams and river networks in the area come from precipitation, runoff, and rivers upstream. The flowing river provides a source of fresh drinking water and nutrients for soils, supporting life in and around the area. However, urbanization, climate change and poor landuse can diminish the capacity and potential of watersheds to support life.
SIGNIFICANCE OF WATERSHEDS
Sustainable human development requires access to water for domestic, agricultural and industrial purposes. Similarly, growing food requires good soil with the right balance of nutrients. This establishes the linkages between watershed health and human development. Watersheds are affected by climate change which can reduce the quantity, quality, timing and distribution of water. The cumulative impacts of past land-uses, water withdrawals, and disturbances in a watershed are all exacerbated by climate change (3). Effective watershed management is essential for several reasons:
Water Supply: Watersheds are the source of our drinking water, irrigation for agriculture, and water for industrial use.
Flood Control: Proper management can help mitigate floods by reducing runoff and soil erosion.
Water Quality: Protecting watersheds helps maintain water quality by preventing pollution and sedimentation.
Biodiversity Conservation: Healthy watersheds support diverse ecosystems, including plants, animals, and microorganisms.
Economic Development: Sustainable watershed management can contribute to economic growth by supporting agriculture, tourism, and other industries.
Climate Resilience: Mitigating the adverse effects of extreme climatic conditions, such as drought and desertification, on crops, humans, and livestock.
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT PROJECTS FOR WATER AND FOOD SECURITY IN NIGERIA
In Nigeria, the Federal Government in collaboration with development partners such as the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), Africa Development Bank (AfDB) and World Bank has ramped up investments in developing agriculture and water resources. For example, the World Bank is supporting the development of dams for irrigation and power generation through the Sustainable Power and Irrigation in Nigeria (SPIN). Similarly, the Special Agro-Industrial Processing Zone (SAPZ) program, as well as the Value Chain Development Program (VCDP) were launched by the AFDB and IFAD respectively.
While these programs are significant and undergo extensive environmental and social screening before approval, integrated watershed management is not well-aligned with their development objectives. Pranay Panjala and his co-workers from the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) evaluated Nigeria’s watersheds and determined that there were up to 277 watersheds across the country. The researchers used a multi-criteria dataset of biophysical parameters including temperature, precipitation, slope, soil depth, soil texture, and length of growing period to establish that only 57 out of the 277 watersheds in Nigeria were suitable and prime for economic development. Their result also implies that the remaining 220 (covering more than 70% of the country) had some type of limitation across the biophysical parameters which does not guarantee economic value without innovative and sustainable measures. Accordingly, poor management of watersheds in Nigeria will increase human vulnerability to hunger, disasters and other environmental challenges.
KEY PRINCIPLES OF WATERSHED MANAGEMENT
Modern watershed management practice requires an integrated approach providing a holistic consideration for the interconnectedness of various factors, including land use, water resources, and ecological processes. Also, engagement and participation is comprehensive. Involving local communities in decision-making processes ensures ownership and sustainability of management practices. Other key principles of watershed management include:
- Sustainable Land Use: Promoting sustainable land use practices, such as agroforestry, conservation agriculture, and reforestation, helps protect soil and water resources.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water conservation measures, like efficient irrigation techniques and rainwater harvesting, helps reduce water consumption.
- Pollution Control: Controlling pollution from point and non-point sources is crucial for maintaining water quality.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation of watershed health and management practices are essential for adaptive management.
THE CHALLENGES AND OPPORTUNITIES
Nigeria’s agricultural and water resources sectors present a wealth of development opportunities, driven by the country’s vast land, favorable climate, and growing population. However, there is growing concern about the impacts of climate change, casting a shadow of challenges. Increased population and urbanization as well as loss of forest cover and land degradation are increasing surface temperatures, soil erosion and water scarcity.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities to improve watershed management:
Technological Advancements: New technologies, such as remote sensing and GIS, can enhance monitoring and decision-making.
Policy and Institutional Reforms: Strong policies and effective institutions are essential for implementing sustainable watershed management practices.
Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the importance of watersheds and promoting environmental stewardship can drive behavioural change.
CONCLUSION
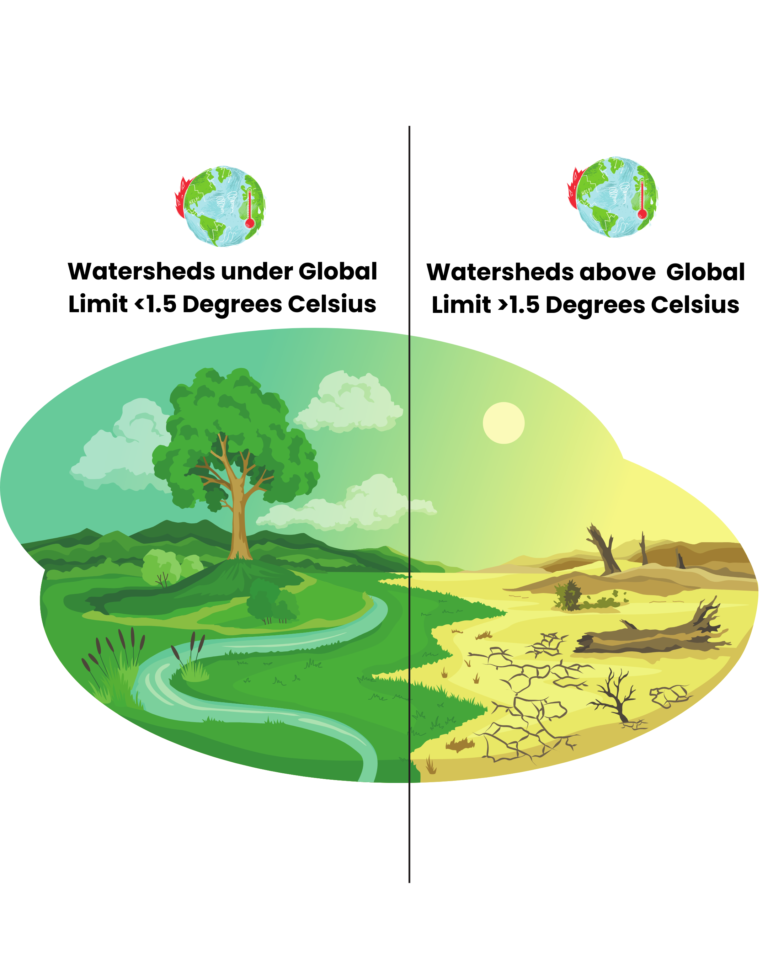
Climate change is now intricately linked to watershed development, influencing hydrological processes, water availability, and ecological balance. As the climate warms, precipitation patterns become increasingly erratic, leading to more frequent and intense rainfall events and prolonged droughts. These shifts disrupt the delicate equilibrium of watersheds, affecting water flow, sediment transport, and nutrient cycling. In response to these challenges, sustainable development programs must now adapt their climate change plans to include integrated watershed management. This involves implementing climate-resilient strategies, such as sustainable land use practices, water conservation measures, and infrastructure upgrades, aligning with global climate goals and protecting vital ecosystems.
REFERENCES
- Amangabra, G.T. & Obenade, M., Flood vulnerability assessment of Niger Delta states relative to 2012 flood disaster in Nigeria. American Journal of Environmental Protection, 3(3), pp. 76–83, 2015
- Nura Umar and Alison Gray, 2022. Flooding in Nigeria: a review of its occurrence and impacts and approaches to modelling flood data. International Journal of Environmental Studies 2023, VOL. 80, NO. 3, 540–561 https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2022.2081471
- Vinay Harswal (2019): Importance of Watershed Development in Water Resources Management. Link: https://waterforpeopleindia.org/importance-of-watershed-development-in-water-resources-management/


